목차
- Stack과 Queue
- Stack과 Queue 메서드
- Stack과 Queue의 활용예제
Stack과 Queue
스택(Stack): LIFO(Last in First Out)구조. 마지막에 저장된 것을 제일 먼저 꺼내게 된다.
- push(저장)
- pop(추출)
큐(Queue): FIFO(First in First)구조. 제일 먼저 저장한 것을 제일 먼저 꺼내게 된다.
- offer(저장)
- poll(추출)
스택을 구현하려면 배열, 큐를 구현하기에는 링크드 리스트가 효율적이다.
스택 클래스의 메서드
Stack stack = new Stack();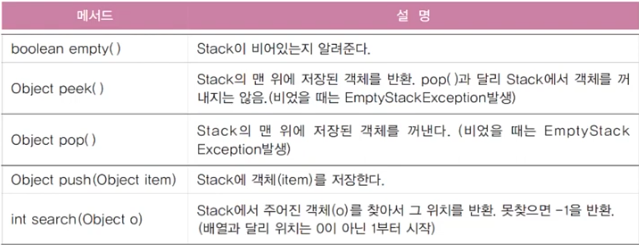
큐 인터페이스의 메서드
Queue que = new LinkedList();
큐를 구현한 클래스 찾기
큐는 인터페이스이기 때문에 큐를 구현한 적절한 클래스를 찾아서 객체를 만들면 된다.
1. 큐를 직접 구현한다.
2. 큐를 구현한 클래스를 사용한다. (Java API)

public class Ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack st = new Stack();
Queue q = new LinkedList(); // Queue 인터페이스의 구현체인 LinkedList
st.push(new Integer(0));
st.push(Integer.valueOf(1));
st.push("2");
q.offer("0");
q.offer("1");
q.offer("2");
System.out.println("== Stack ==");
while (!st.empty()) {
System.out.println(st.pop()); // 스택에서 요소 하나를 꺼낸다.
}
System.out.println("== Queue ==");
while (q.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(q.poll()); // 큐에서 요소 하나를 꺼낸다.
}
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println(q.remove()); // 큐에서 요소 하나를 꺼낸다.
} catch (NoSuchElementException ne) {
System.out.println("끝");
break;
}
}
}
}== Stack ==
2
1
0
== Queue ==
0
1
2
끝
스택과 큐의 활용
스택의 활용 예 - 수식계산, 수식괄호검사, 워드프로세서의 undo/redo, 웹브라우저의 뒤로 / 앞으로
큐의 활용 예 - 최근사용문서, 인쇄작업 대기목록, 버퍼(buffer)
public class Ex2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack st = new Stack();
String expression = "((3 + 5) * 8 - 2))))";
System.out.println("expression = " + expression);
try {
for (int i = 0; i < expression.length(); i++) {
char ch = expression.charAt(i);
if (ch == '(') {
st.push(ch); // 오토박싱 지원 ch + ""
} else if (ch == ')') {
st.pop(); // ')' 이 더 많으면 Exception을 터트림
}
}
if (st.isEmpty()) { // '(' 많으면 else를 출력 스택에 '('이 남아있을 뿐 없는 것을 꺼내는게 아니기 때문에
System.out.println("괄호가 일치합니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("괄호가 일치하지 않습니다.");
}
} catch (EmptyStackException e) {
System.out.println("괄호가 일치하지 않습니다.2");
}
}
}expression = ((3 + 5) * 8 - 2))))
괄호가 일치하지 않습니다.2
public class Ex3 {
static Queue q = new LinkedList();
static final int MAX_SIZE = 5;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("help를 입력하면 도움말을 볼 수 있습니다.");
while (true) {
System.out.print(">>");
try {
// 화면으로부터 라인단위로 입력 받는다.
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
String input = s.nextLine().trim(); // 공백 잘라서 입력받은 값을 넣음
if ("".equals(input)) {
continue;
}
if (input.equalsIgnoreCase("q")) {
System.exit(0);
} else if (input.equalsIgnoreCase("help")) {
System.out.println(" help - 도움말을 보여줍니다.");
System.out.println(" q 또는 Q - 프로그램을 종료합니다.");
System.out.println(" history - 최근에 입력한 명령어를 " + MAX_SIZE + "개 보여줍니다.");
} else if (input.equalsIgnoreCase("history")) {
save(input); // 입력받은 명령어를 저장하고,
// LinkedList의 내용을 보여준다.
LinkedList list = (LinkedList) q;
// for문으로 list.size를 반복할 필요가 없으니 상수처리해서 for문에 넣어줬다.
final int SIZE = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
System.out.println((i + 1) + ". " + list.get(i));
}
} else {
save(input);
System.out.println(input);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("입력 오류입니다.");
}
}
}
public static void save(String input) {
// queue에 저장한다.
if (!"".equals(input)) { // if(input!.equals(null) && !input.equals("") )
q.offer(input);
}
// queque의 최대 크기를 넘으면 제일 처음 입력된 것을 삭제한다.
if (q.size() > MAX_SIZE) { // size()는 Collection 인터페이스에 정의
q.remove();
}help를 입력하면 도움말을 볼 수 있습니다.
>>help
help - 도움말을 보여줍니다.
q 또는 Q - 프로그램을 종료합니다.
history - 최근에 입력한 명령어를 5개 보여줍니다.
>>나는
나는
>>쌈뽕
쌈뽕
>>코딩이야
코딩이야
>>반가워
반가워
>>history
1. 나는
2. 쌈뽕
3. 코딩이야
4. 반가워
5. history
>>
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] Arrays - 배열을 쉽게 다루고 싶다면 (0) | 2024.05.07 |
|---|---|
| [Java] Iterator, Listlterator, Enumeration (0) | 2024.05.07 |
| [Java] LinkedList 특징 (0) | 2024.05.06 |
| [Java] 컬렉션 프레임워크, ArrayList (0) | 2024.05.05 |
| [Java] Arrays로 배열 다루기 (0) | 2024.05.02 |


